In the medical field, disinfection and sterilization are an indispensable part of preventing and controlling hospital infections. It is crucial to have a deep understanding of the classification of microorganisms, clarify the definition and principles of disinfection and sterilization, and be proficient in common disinfection and sterilization methods and precautions to ensure the health and safety of patients and medical staff.
1. Classification of Microorganisms
Microorganisms are a type of tiny organisms that are widely present in nature. They are numerous and numerous, with a total number of more than hundreds of thousands. Based on their size, structure and composition, microorganisms can be roughly divided into three categories: non-cellular microorganisms, prokaryotic cell-type microorganisms and eukaryotic cell-type microorganisms.
Non-cellular organisms: subviruses, viruses
Prokaryotes: bacteria, actinomycetes, cyanobacteria, mycoplasmas, chlamydia, rickettsia.
Eukaryotes: fungi, protozoa, unicellular algae
 2.Definition and principles of disinfection and sterilization
2.Definition and principles of disinfection and sterilization
Disinfection: refers to the process of killing or removing pathogenic microorganisms on the transmission medium to make it harmless. The main purpose of disinfection is to reduce or eliminate the number of pathogenic microorganisms and reduce the risk of infection.
Sterilization: refers to the process of killing or removing all microorganisms (including bacterial spores) on the transmission medium. Sterilized items are called "sterile items" and are mainly used for medical equipment that needs to enter the human body, including entering the blood, tissues, and body cavities, such as surgical instruments, injection equipment, etc.
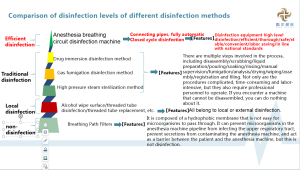
3. Disinfection Level
1. Sterilization level:
Definition: Kill all microorganisms including bacterial spores to achieve sterility assurance level.
Common methods include pressure steam sterilization/dry heat sterilization, ethylene oxide, hydrogen peroxide low-temperature plasma, low-temperature formaldehyde sterilization, etc.
2. High-level disinfection:
Definition: Kill all bacterial propagules including mycobacteria, viruses, fungi and their spores and most bacterial spores.
Common methods include using chlorine-containing preparations, chlorine dioxide, o-phthalaldehyde, peracetic acid, hydrogen peroxide, ozone, iodine tincture, etc. and chemical disinfectants that can achieve sterilization effects under specified conditions, with appropriate concentrations and effective action time for disinfection.
3. Medium-level disinfection:
Definition: Medium-level disinfectants can kill mycobacteria, bacterial propagules, most viruses and most fungi, but cannot kill bacterial spores.
Commonly used methods include the use of iodine disinfectants (iodine tincture, chlorhexidine iodine, etc.), alcohol and chlorhexidine compound, alcohol and quaternary ammonium salt compound, phenol and other disinfectants, under specified conditions, with appropriate concentrations and effective action time for disinfection.
4. Low-level disinfection:
Definition: It can kill bacterial propagules, lipophilic viruses, etc., but cannot kill fungi and Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and cannot inactivate hepatitis B virus, etc.
Commonly used methods include the use of quaternary ammonium salts (benzalkonium bromide, etc.), biguanides (chlorhexidine) and other disinfectants.
4. Common methods of disinfection and sterilization
Hospital disinfection and sterilization methods mainly include two categories: physical disinfection and sterilization and chemical disinfection and sterilization.
Physical disinfection and sterilization
① Dry heat disinfection and sterilization: disinfection through dry hot air, suitable for heat-resistant but not moisture-resistant items. Generally, propagules can be killed in dry heat of 80-100℃ for 1 hour, and spores can be killed at 160-170℃ for 2 hours. Commonly used methods include burning and dry baking.
② Moist heat disinfection and sterilization: including boiling and high-pressure steam sterilization. Moist heat disinfection and sterilization has fast heat transfer and strong penetration due to the heat conduction of air and water vapor, and requires lower temperature and shorter time. Boiling method is suitable for high-temperature resistant items, and high-pressure steam sterilization is widely used for sterilization of various medical equipment.
③ Radiation disinfection: use ultraviolet rays, ionizing radiation, etc. to kill microorganisms. Ultraviolet air sterilizers are often used for indoor air disinfection, but it should be noted that ultraviolet rays are harmful to the human body. It is necessary to ensure that no one is present during disinfection.
④ Microwave disinfection: use the thermal effect and comprehensive effect of high-frequency electromagnetic waves for sterilization. Suitable for disinfection of food, medicines and certain medical equipment.
Chemical disinfection and sterilization
① Chlorine-containing preparations: such as sodium hypochlorite and chlorine dioxide, which can effectively kill a variety of pathogenic microorganisms, but it should be noted that they are corrosive to metals, and the concentration and action time should be controlled when used.
② Peroxide disinfectants: Peroxide disinfectants, such disinfectants include peracetic acid, hydrogen peroxide, chlorine dioxide and ozone. Peracetic acid and hydrogen peroxide are often used for indoor air disinfection and surface disinfection. Ozone is a highly effective disinfectant that can kill various microorganisms. Ozone gas or aqueous solution has a strong effect of killing microorganisms. It is often used for drinking water disinfection, sewage treatment, air disinfection and surface disinfection of objects.
③ Aldehyde disinfectants: such as glutaraldehyde, have a strong killing effect on bacterial spores, but they need to be thoroughly cleaned before use to prevent residues from causing harm to the human body.
④ Alcohol disinfectants: mainly ethanol, isopropanol, n-propanol or a compound preparation of the two components. It is often used for hand and skin disinfection, and can also be used for the disinfection of smaller object surfaces. But it is not suitable for the disinfection of grease and smooth surfaces.
⑤ Iodine-containing disinfectants: including iodine and various preparations with iodine as the main bactericidal component. Iodine tincture is a complex iodine disinfectant made of iodine and potassium iodide, which is suitable for surgical hand and skin disinfection, surgical incision site, injection and puncture site skin and newborn umbilical cord site skin disinfection, mucosal flushing disinfection, hygienic hand disinfection, etc.